![]()
Mr. Clifford’s app is now available at the App Store and Google play. His mobile app is perfect for students in AP macroeconomics or college introductory macro courses. It is designed to help you ace the exam, final, or AP test.
The app includes over 60 new economics videos that are not available on YouTube. These videos explain complex concepts in a student-friendly, easy to understand manor that will help you retain the information.
Join the hundreds of thousands of students that have used Mr. Clifford’s videos and resources to ace your macroeconomics course….(read more)
HOW TO: Hedge Against Inflation
REVEALED: Best Investment During Inflation
HOW TO INVEST IN GOLD: Gold IRA Investing
HOW TO INVEST IN SILVER: Silver IRA Investing
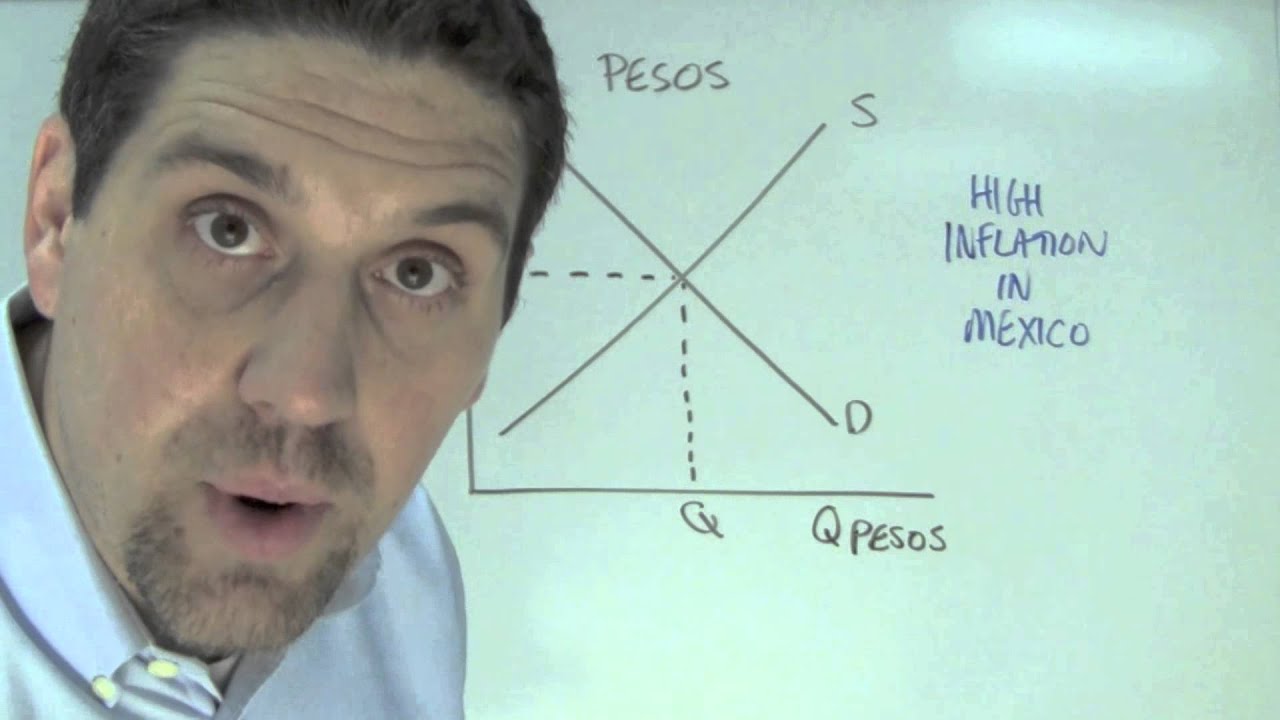
Macro Unit 5, Question 6 revolves around exchange rate and inflation. The exchange rate is the value of one currency in relation to another. Inflation is the continuous increase in prices of goods and services in an economy over time. The relationship between the exchange rate and inflation is a crucial one to understand as it can have several impacts on an economy.
Firstly, higher inflation rates can lead to a decrease in the exchange rate of a currency. This is because higher inflation reduces the purchasing power of individuals and businesses in that country, causing the demand for goods and services to decrease. Consequently, this leads to a lower demand for the country’s currency, causing the exchange rate to fall.
Secondly, a decrease in the exchange rate can cause inflation to rise. This is because it makes imports more expensive, which can lead to higher prices of goods and services. Additionally, a lower exchange rate can encourage domestic producers to export more, leading to a decrease in the supply of goods and services in the local market. This decrease in supply leads to higher prices, causing inflation to rise.
Thirdly, a high exchange rate can lead to deflation in the economy. This is because a high exchange rate makes imports cheaper, which can lead to increased competition for domestic producers. This increased competition causes a decrease in the prices of goods and services, leading to deflation.
Finally, a high exchange rate can lead to a decrease in the inflation rate. This is because a higher exchange rate makes imports cheaper, causing the price of goods and services to decrease. This decrease in prices causes a decrease in the inflation rate.
In conclusion, there is a clear relationship between exchange rate and inflation. A change in one can have significant impacts on the other. It is essential for policymakers and investors to understand this relationship and take appropriate measures to manage both.


Best explanation I've had yet. Thank you
is this video so quick coz it's for people who went to the restroom during the final exam? lmao
2020. This is on steroids right now.
Answered my question
Wow never seen someone explains something so good this fast .
which exchange rate used in this video? nominal or real?
If a domestic currency deppreciaton is linked with the country's increased inflation.. do you agree that Price decrease to foreigners since they need less of their currency to buy this domestic currency? In such case I don't understand the phrase "Inflation in the U.K., by itself, increases the real $/£ exchange rate so that a unit of real
goods and services in the U.K. costs relatively more in USD than it did at the base period."
Thank you for explaining this
thnk u sooo much for ths.
far out, you're amazing
Cool, THANKS!!!
I also think that it is good. I am from South Africa
Wow thanks for this! I'm from Singapore here and i really understand your lectures!