► Receive Full Free Stocks via Moomoo (T&C Apply): Up to 15 Free Stocks via Moomoo US (For Australian users, up to 10 Free Stocks for A$2K deposit), T&C Apply:
► How I went from Zero To A Million:
► My Stock Portfolio + Stock Tracker:
► Get 2 FREE stocks valued up to $1850 (when you deposit $100):
► ROBINHOOD (Get 1 Stock When You Sign Up):
► Open A Roth IRA:
► Follow Me On Instagram:
► How I Protect My Bitcoin:
My PO Box:
Andrei Jikh
4132 S. Rainbow Blvd # 270
Las Vegas, NV 89103
*None of this is meant to be construed as investment advice, it’s for entertainment purposes only. Links above include affiliate commission or referrals. I’m part of an affiliate network and I receive compensation from partnering websites. The video is accurate as of the posting date but may not be accurate in the future.
#shorts #investing #finance…(read more)
LEARN MORE ABOUT: IRA Accounts
TRANSFER IRA TO GOLD: Gold IRA Account
TRANSFER IRA TO SILVER: Silver IRA Account
REVEALED: Best Gold Backed IRA
Title: How The Banks Collapsed: A Historical Overview #shorts
Introduction:
In recent history, the phrase “bank collapse” has become synonymous with global economic downturns, uncertainty, and mistrust in financial institutions. The collapse of banks has severe consequences that ripple through the economy, affecting businesses, individuals, and governments alike. This article aims to delve into the causes and effects of such collapses, shedding light on the reasons behind their occurrence and providing a historical overview.
1. The Great Depression and the Collapse of Banks:
One of the most significant instances of bank collapse occurred during the Great Depression in the 1930s. The stock market crash in 1929 triggered a chain reaction leading to the bankruptcy of numerous banks. The excessive lending practices, lack of regulation, and over-speculation in the market left banks extremely vulnerable. As panicked depositors raced to withdraw their savings, banks faced immense liquidity pressure, culminating in their eventual collapse.
2. The Housing Bubble and the 2008 Financial Crisis:
Skipping forward several decades, the collapse of banks during the 2008 financial crisis rocked the global economy to its core. Prior to the crisis, banks relaxed their lending standards, primarily in the housing market, leading to an unsustainable housing bubble. When the bubble inevitably burst, banks were left holding a vast number of toxic assets, primarily backed by risky mortgages. The collapse of prominent institutions like Lehman Brothers sparked a domino effect, resulting in a severe credit crunch, bailouts, and a global recession.
3. Currency Crises and Bank Failures:
From the Mexican peso crisis in the 1990s to the Asian financial crisis in the late 1990s, currency fluctuations have played a significant role in bank collapses. Currency crises erode investor and depositor confidence, often leading to bank runs and subsequent failures. These crises are typically triggered by sudden changes in economic factors, such as inflation rates or government policies.
4. Lack of Regulation and Oversight:
One common thread running through many bank collapses is the lack of adequate regulation and oversight. Banks engaging in high-risk activities, combined with lenient supervision from regulators, often create a dangerous concoction of potential failure. Without proper checks and balances, banks may be more inclined to take excessive risks, leading to a higher likelihood of collapse.
Conclusion:
The collapse of banks has been an unfortunate recurring theme throughout history, casting a shadow on the global economy and leaving millions suffering from the consequences. Whether triggered by stock market crashes, housing bubbles, currency crises, or inadequate regulation, these collapses result in severe financial instability, job losses, and economic recessions. Governments and regulatory bodies must learn from history and implement robust measures to prevent, or at least minimize, the chances of future bank collapses. By fostering transparency, enforcing strong regulation, and conducting regular stress tests, we can work towards a more stable economic future.

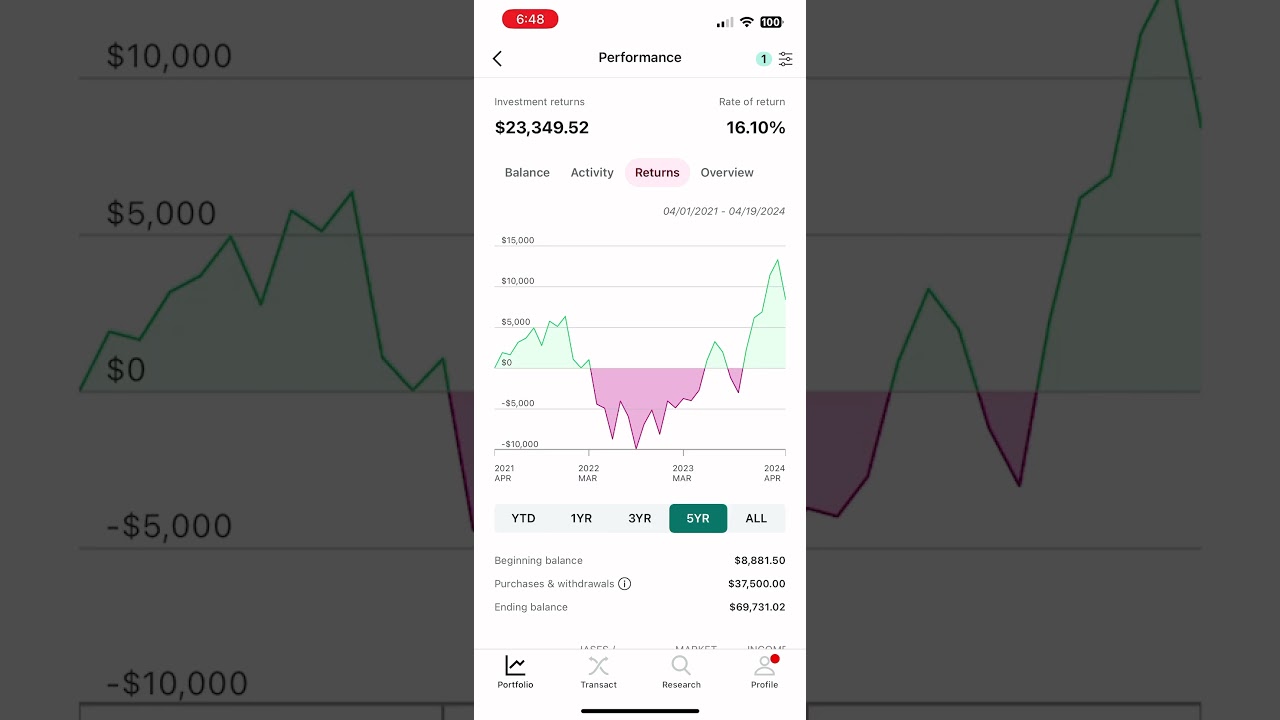
it was due to bad regulation and stupidity having all your money into one avenue. When the Federal Reserve hiked interest rates in 2022 to combat inflation, SVB's bond portfolio started to drop. SVB would have recovered its capital if they held those bonds until their maturity date. but because they had all there funds there they couldnt take the bank run.